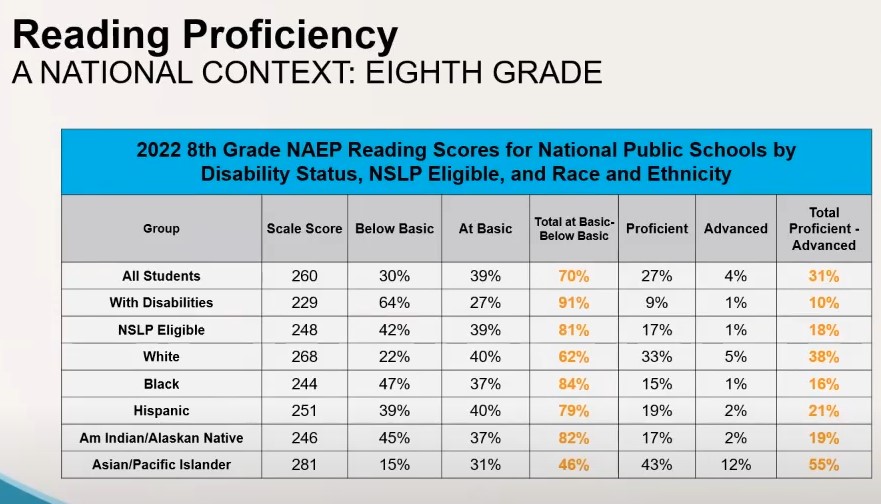
49.13% 77% SED, 26% EL
28.35% 84% SED, 45% EL
40.51% 81% SED, 37% EL
44.17% 74% SED, 19% EL
52.37% 57% SED, 11% EL
51.37% 27% SED, 0% EL
39.38% 74% SED, 27% EL
50.79% 95% SED, 32% EL
20.80% 93% SED, 50% EL
70.37% 46% SED, 8% EL
33.34% 90% SED, 38% EL
58.82% 55% SED, 9% EL
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 26% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 24% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 27% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 23% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 40% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 32% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 18% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 10% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 34% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 26% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 24% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 16% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 31% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 25% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 29% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 15% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 25% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 23% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 25% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 27% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 19% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 30% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 32% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 19% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 33% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 28% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 20% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 19% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 22% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 27% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 31% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 20% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 50% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 29% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 17% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 4% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 13% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 16% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 26% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 45% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 39% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 28% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 23% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 10% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 19% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 22% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 22% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 37% |
49.13% 77% SED, 26% EL
28.35% 84% SED, 45% EL
40.51% 81% SED, 37% EL
44.17% 74% SED, 19% EL
52.37% 57% SED, 11% EL
51.37% 27% SED, 0% EL
39.38% 74% SED, 27% EL
50.79% 95% SED, 32% EL
20.80% 93% SED, 50% EL
70.37% 46% SED, 8% EL
33.34% 90% SED, 38% EL
58.82% 55% SED, 9% EL
49.13% 77% SED, 26% EL
28.35% 84% SED, 45% EL
40.51% 81% SED, 37%
44.17% 74% SED, 19% EL
52.37% 57% SED, 11% EL
51.37% 27% SED, 0% EL
39.38% 74% SED, 27% EL
50.79% 95% SED, 32% EL
20.80% 93% SED, 50% EL
70.37% 46% SED, 8% EL
33.34% 90% SED, 38% EL
58.82% 55% SED, 9% EL
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 26% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 24% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 27% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 23% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 40% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 32% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 18% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 10% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 22% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 27% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 31% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 20% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 50% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 29% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 17% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 4% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 31% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 25% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 29% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 15% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 25% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 23% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 25% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 27% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 19% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 22% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 22% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 37% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 33% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 28% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 20% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 19% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 13% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 16% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 26% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 45% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 19% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 30% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 32% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 19% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 39% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 28% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 23% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 10% |
| English Language Arts/Literacy | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Standard Not Met (Level 1) | 34% |
| Standard Nearly Met (Level 2) | 26% |
| Standard Met (Level 3) | 24% |
| Standard Exceeded (Level 4) | 16% |
 | Meet or Exceed State Standard | Socio-Economic Disadvantaged Students (% of population) | English Learners (% of population) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEABODY* | 70 | 46 | 8 |
| ROOSEVELT | 52 | 57 | 11 |
| WASHINGTON** | 59 | 55 | 9 |
| SB CHARTER | 51 | 27 | 0 |
| ADAMS | 49 | 77 | 26 |
| MONROE | 44 | 74 | 19 |
| ADELANTE *** | 39 | 74 | 27 |
| FRANKLIN | 51 | 95 | 32 |
| HARDING **** | 41 | 81 | 37 |
| CLEVELAND | 28 | 84 | 45 |
| SB COMMUNITY ACADEMY | 33 | 90 | 38 |
| MCKINLEY***** | 21 | 93 | 50 |